Joint pain, stiffness, and trouble doing daily tasks are common symptoms of arthritis and osteoarthritis (OA), which affect millions of people everywhere. Some people need surgery to get rid of their pain and regain independence, even though medications, exercises, and changes to their lifestyle can help. In this guide, we will talk about the leading surgical solutions for arthritis and osteoarthritis in a way that is easy to understand.
Many people have arthritis; more than 350 million people worldwide have it. Nearly 78 million people in the United States will have arthritis by 2040, up from the current 58.5 million. Osteoarthritis is the most common type. It hurts and makes you stiff, and it also affects your everyday life, work, and health in general. When you look at these numbers, you can see how important early treatment and, in some cases, surgery are.
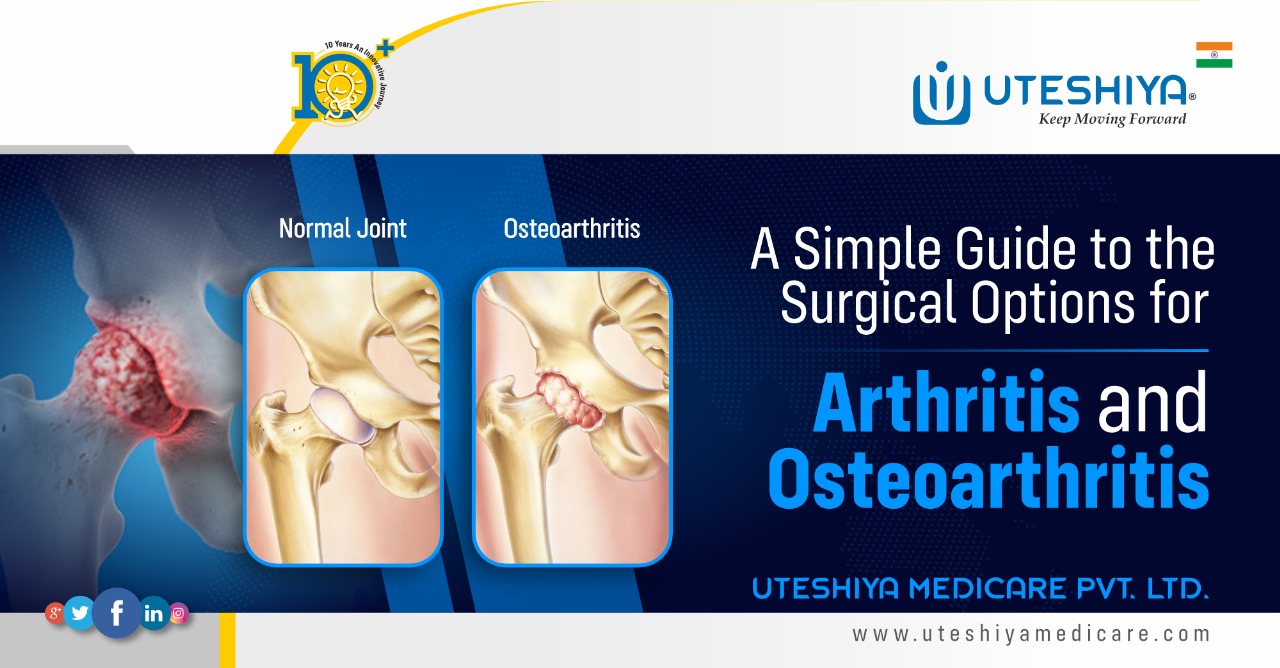
How to Understand Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
Inflammation of the joints causes arthritis, making them swell, stiff, and hurt. Osteoarthritis is the most common type. It happens when the cartilage that protects your joints goes away over time.
Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks the joints, leading to long-lasting swelling and damage. Rheumatoid arthritis can happen to people of any age, but osteoarthritis is more common in older adults.
Why Should Surgery Be Needed?
When pain gets too bad and gets in the way of daily life, surgery is often thought of. It’s also a choice if medication, physical therapy, and other non-surgical methods don’t help. Additionally, people with severe joint damage or defects may benefit from surgery. If surgery is the best option for your situation, it requires talking to an orthopedic specialist.
What Are the Common Surgical Options?
Arthroscopy is a painless process in which a small camera is put into the joint through tiny cuts. Then, surgeons can remove damaged tissue, smooth out rough spots, and fix minor joint problems. Many people with slight to moderate arthritis have this kind of surgery on their knees, hips, and ankles.
Joint replacement (arthroplasty) removes and replaces a damaged joint with an artificial one. Total knee and hip replacements are most common. These surgeries relieve pain, restore movement, and improve quality of life. Modern implants usually last 15–20 years, though durability depends on activity level and joint type.
Arthrodesis, another name for joint fusion, stops movement and eases pain by joining the bones in a joint together. This process can help when it’s impossible to replace a joint or when it is not stable. However, fusion does restrict mobility in the affected joint, despite its ability to reduce the pain.
Osteotomy, which means removing and repositioning bones, is used to realign bones and move weight away from a damaged joint. This minimizes the pain and slows the development of arthritis. Osteotomy is often suggested for younger, busy people with early osteoarthritis, especially in the knees.
The synovectomy procedure removes the synovial membrane, which is the swollen lining of a joint. This can help lower discomfort and stiffness, especially in people with early-stage inflammatory arthritis who don’t get better with medicine.
How Are Less Invasive Treatments Helping?
There are now less invasive choices because of recent medical progress. People who aren’t ready or able to have major surgery may be able to get these methods instead.
- Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE): This is a minor procedure that blocks some arteries to lower swelling in the knee.
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA): This method kills nerves in the joint that send pain messages.
- Viscosupplementation Injections: Hyaluronic acid injections can help ease pain and keep the joint lubricated, but effects may vary.
Getting Better After Surgery
No matter what surgery you had, physical therapy is essential to getting stronger, moving better, and being more flexible. Managing pain with medicine or easy techniques like ice or heat treatment can help the body heal.
Keeping a healthy weight, avoiding high-impact activities, and using assistance devices as needed are all changes that can be made to protect the joint and make the effects of surgery last longer. For long-term success, you must follow your doctor’s plan for your recovery.
Tips to Prevent Arthritis Progression
Taking care of your joints is important to keep arthritis from worsening, even after surgery.
- Keeping a healthy weight makes your joints less stressed.
- Swimming, cycling, or walking are gentle, low-impact workouts that can help strengthen muscles and make joints more flexible.
- Avoiding high-impact activities you do repeatedly and ensuring a good balance can also help protect your joints.
- Eating a varied diet full of foods that reduce inflammation, like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can also help keep your joints healthy.
How to Choose a Surgeon and Prepare for Surgery
It is very important to choose the right orthopedic surgeon. Look for a specialist who has done the procedure you need and has a proven record of success. You can be sure of your choice if you read reviews from other patients, ask for recommendations, and discuss your concerns freely during consultations.
Surgical healing is faster if you are appropriately prepared. Your doctor may give you tests to ensure you are healthy for surgery. Following the directions for your medicines, diet, and activities is essential. Getting your home ready for the first few weeks after surgery can make things much easier. For example, you can organize essential items, set up adaptive devices, and make a comfortable healing space.
Mental readiness matters too. Knowing realistic recovery times, what to expect from physical therapy, and how things will get better over time can help lower anxiety. Talking to people who have been through the same thing or joining a support group can give you hope and helpful advice.
Wrapping It Up
Surgery for arthritis and osteoarthritis can help with pain and make it easier to move everywhere. The best treatment for you depends on your age, activity, and how badly your joints hurt. An orthopedic expert can help you determine the best way to treat your condition. Modern surgery and the proper care afterward help many people get back to a busy lifestyle and enjoy life with less pain.